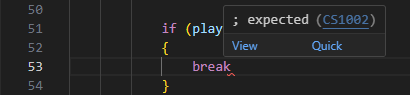
The error messages in Visual Studio Code are self-explanatory but if you don't know where to look at it can be pretty confusing. In the above example, the error message is telling us that there's a missing semi-colon in line 53.
The error message also tells us the file name and the line number where the error is located.
Since VS Code is trying to be precise, it's pointing the exact location where the error occurred. "53" is the line number where the error is located.
"22" is the column number within that line where the error is expected.
The error message also tells us the type of error. In this case, it's a syntax error. The error message also tells us the error code. In this case, it's CS1002.The error message also tells us the error type. In this case, it's a syntax error. The error message also tells us the error description. In this case, it's telling us that it's expecting a semi colon on the line.
There's also a red squiggly line under the line where the error is located. This is another way of telling us that there's an error in the code. If you hover over the red squiggly line, it will tell you the same thing as the error message.