As one of the most widely distributed texts, Microsoft Word documents will be used by a number of individuals with accessibility needs. Word has built in features to accommodate many accessibility solutions for those with sighted disabilities. Word also comes equipped with a Check Accessibility review item that will identify any issues you may have missed when checking for accessibility.
Heading structures not only organize writing into digestible sections for sighted users, but it is important for those with screen readers and other assistive technologies to understand the hierarchal structure and reading order of the content. Word comes with a Styles Plane located on the right side of the toolbar in the Home tab. This feature will help you label the document's title, level headings, body text, and other forms of structural content.
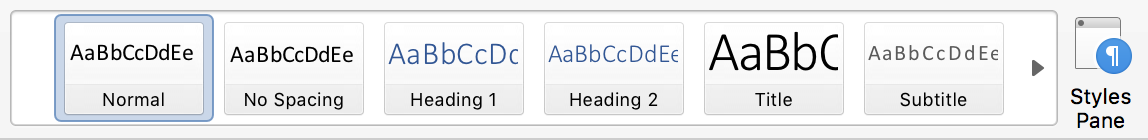
Headings are used to denote the hierarchy of the page's content as follows:
You may modify the headings to any font, size, and style you desire, but this is only for sighted users. Those with screen readers or other assistive technologies will only understand the hierarchy of the page's content.
For more details on headings, visit the Accessibility Basics page.
Lists add important hierarchical structure to a document. While this provides visual structure for sighted users, it does not provide the document structure needed for assistive technology users. There are two types of lists in Word: ordered and unordered.
Ordered (numbered) lists are used to identify a group of items that follow a sequence checklist.
Example:Unordered (bulleted) lists are used for a group of items without a sequence.
Example:Hyperlinks in Word documents allow users to visit web pages, navigate to Wordheadings, and open email links. Sighted users can readily identify links because of their blue color or by hovering over them, but users requiring assistive technology scan documents looking for alternate text. These links should convey clear information of where the link takes them.
Word will automatically create hyperlinks when you paste a URL into a document and hit Enter or Tab. The created link will display the URL as the display text (e.g., http://auburn.edu/eaccessibility ), but you will need to edit Word's default link text so users with sight disabilities can access them.
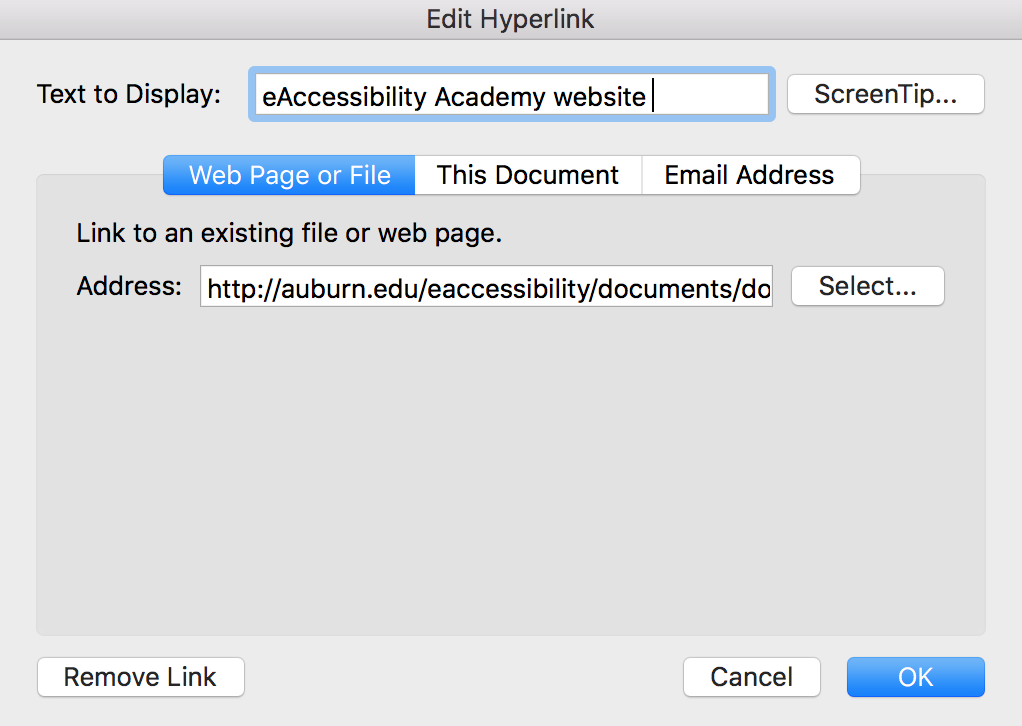
To create accessible links:
Images are useful visuals for sighted users to grasp larger concepts or to show examples. For those with accessibility needs, you will need to write alternative text for images to provide a non-visual means of representing the image's content or purpose. When alt text is added correctly to an image, screen reading software can read it in a Word, PDF, or HTML file.
Image types in Word documents that can be given Alternative Text include:
To write Alternative Text:
Tips for writing Alternative Text:
Videos and audio files can also be inserted into Word documents without having the user leave the document to view it. The steps for including these files in your document are shown here for different versions of Word.
To insert a video or audio file in Word 2016:
Color is an important accessibility item to consider. Users with sighted disabilities need proper contrast so the text can be legible and readable. If you need to check for your document's color contrast, reference the WebAim Color Contrast Checker or enter your website's URL in the WAVE Web Accessibility Tool.
The purpose of data tables is to present information in a grid, or matrix, and to have columns or rows that show the meaning of the information in the grid.
Sighted users scan a table to make associations between data in the table and their appropriate row and/or column headers. Screen reader users make these same associations with tables in web pages and PDF files. Unfortunately support for table headers is limited in Word. You can add properties to Word documents so that column headers (headers in the first row of the table) are identified by a screen reader and read and when exported to PDF. Unfortunately, row headers (headers in the first column of the table) do not have the same level of support.
Last Updated: July 22, 2025